Diabetes means you have too much sugar in your blood. High blood sugar problem starts when your body no longer makes enough of a chemical, or hormone, called insulin.
Your body changes much of the food that you eat into a type of sugar called glucose.
This sugar travels in your blood to all the cells in your body. Your body cells need the sugar to give you energy.
Insulin helps the sugar to move from your blood into your cells. Without insulin, your cells can’t get the sugar they need to keep you energetic.
By moving sugar from your blood to your body cells, insulin helps to keep your blood sugar level normal (not too high; not too low).
When you don’t have enough insulin to lower high blood sugar levels means you have diabetes.
High blood sugar levels can cause serious health problems
Diabetes can, and must, be treated.
Your body does not make insulin at all
Your body does not make enough insulin, or The insulin that body makes doesn't work right
Blood sugar levels stay high of you don't have enough insulin to move sugar from your blood into your cells.
In type 2 diabetes, the body can make some insulin, but not enough.
Or the insulin, the body makes does not work right
Type 2 diabetes often starts in adults, but children can have too.
It is more common in overweight people or if someone in the family has diabetes.
Several risk factors have been associated with type 2 diabetes and include:
- Age: If your age is 45 yr
- Obesity: If your weight is at higher side
- Family history: If You have a parent or sibling who has diabetes.
- Sedentary lifestyle: If you are inactive or you exercise less than three times in a week.
- Gestational diabetes: If you had diabetes while you were pregnant, this raises your chances of getting type 2 diabetes later in your life.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome: Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have a higher risk.
- Associated comorbid conditions: If you have high blood pressure or high cholesterol or both.
If you consume tobacco or alcohol.
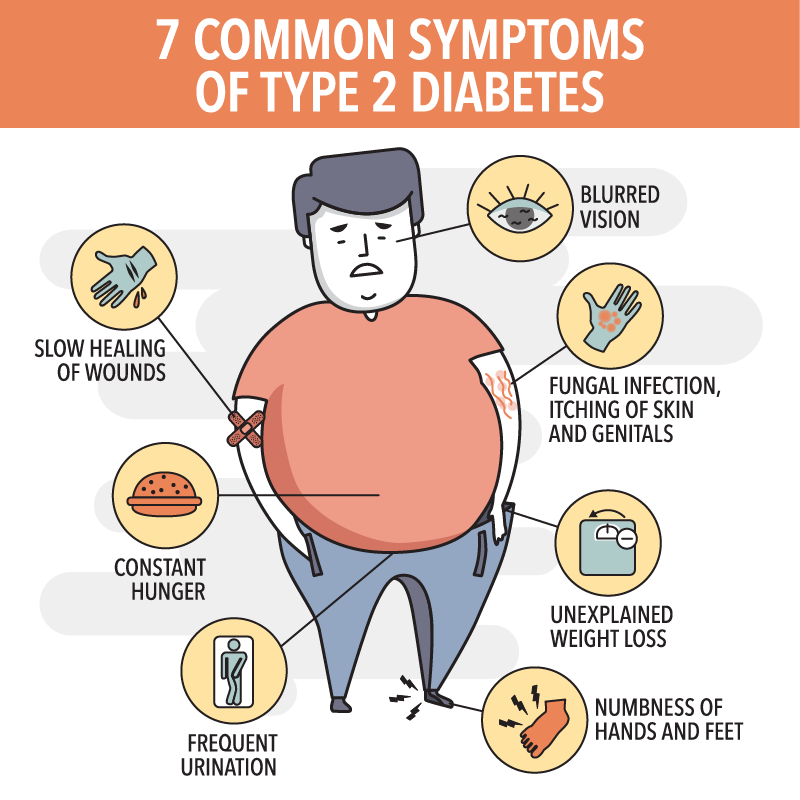
When you have diabetes, excess sugar (glucose) builds up in your blood.
Your kidneys are forced to work overtime to filter and absorb the excess sugar which leads to increased urination.
When you lose sugar through frequent urination, you also lose calories.
At the same time, diabetes may keep the sugar from your food from reaching to your cells — leading to constant hunger.
The combined effect is potentially rapid weight loss.
Excessive thirst (also called polydipsia is classic diabetes symptom.
When you have diabetes, excess sugar (glucose) builds up in your blood.
Your kidneys are forced to work overtime to filter and absorb the excess sugar.
If your kidneys can't keep up, the excess sugar is excreted into your urine, dragging along fluids from your tissues.
This triggers more frequent urination, which may leave you dehydrated.
As you drink more fluids to quench your thirst, you'll urinate even more.
You may feel fatigued. Many factors can contribute to this.
They include dehydration from increased urination and your body's inability to function properly since it's less able to use sugar for energy needs.
High levels of blood sugar for longer period of time can affect the nerves and can lead to poor blood circulation, making it hard for blood needed to reach areas of the body affected by sores and wounds for skin repair
This can lead them to remain open and unhealed for months, increasing the risk of:
- Fungal infections
- Bacterial infections
- Gangrene
Diabetes symptoms sometimes involve your vision.
High levels of blood sugar pull fluid from your tissues, including the lenses of your eyes.
This affects your ability to focus.
Excess sugar in your blood can lead to nerve damage.
You may notice tingling and loss of sensation in your hands and feet, as well as burning pain in your arms, hands, legs and feet.
75 percent of women will have at least one vaginal infection in their lifetime.
There’s a significant link between high blood sugar and vaginal infections.
A number of things can increase your risk of infection, including conditions such as diabetes.
It is estimated that about 35% to 75% of men with diabetes will experience at least some degree of erectile dysfunction or impotence during their lifetime.
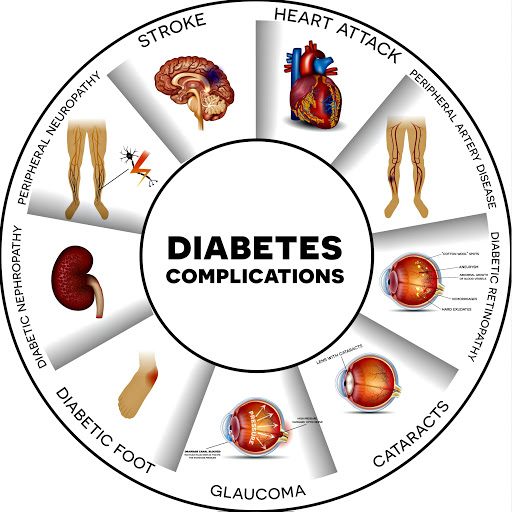
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to a number of short and long-term health complications, including heart disease, nerve damage, amputation, and vision problems.
Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease or stroke by 3 to 4 times than normal person. This includes coronary artery disease with chest pain (angina), heart attack, stroke and narrowing of arteries (atherosclerosis).
Excess sugar can injure the walls of the tiny blood vessels (capillaries) that nourish your nerves, especially in your legs. This can cause tingling, numbness, burning or pain that usually begins from the tips of the toes or fingers and gradually spreads upward.
If left untreated, you could lose all nerve sensation in the affected limbs. Damage to the nerves which are related to digestion can cause problems with nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea or constipation. It may also lead to erectile dysfunction in men.
The kidneys contain millions of tiny blood vessel clusters (glomeruli) that filter waste from your blood. Diabetes can damage this delicate filtering system.
Severe damage can lead to kidney failure or irreversible end-stage kidney disease, which may require dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Diabetes can damage the blood vessels of the retina (diabetic retinopathy), potentially leading to blindness. Diabetes also increases the risk of other serious vision conditions, such as cataracts and glaucoma.
Nerve damage in the feet or poor blood flow to the feet increases the risk of various foot complications. If left untreated, cuts and blisters can develop serious infections, which often heal poorly. These infections may ultimately require amputation of the infected area. Diabetes is the most common cause of amputation.
Diabetes may leave you more susceptible to skin problems, including bacterial and fungal infections.

Diabetes pills help to lower blood sugar and subsequent complications.
There are different types of diabetes pills or tablets. Many of them work in different ways.
Some patients need to take more than one diabetes pill.
Diabetes pills work best when you follow your diet and exercise routine properly
You should:
- Take your diabetes pills at the same time each day
- Refill your stock in advance
- Inform your doctor if you are taking any alternative or herbal medicine
You should not:
- Miss a dose
- Skip a meal
- Stop taking medicine unless advised by doctor
- Take more or fewer pills
Sometimes depending on individual's condition, one may require some other medicines to control or prevent diabetes complications:
- Neuropathy medications- Pain relievers
- Cholesterol medications- Statins
- Blood pressure medications- ACE-I or ARB
- Blood thinners- Aspirin
It increases activity of your body insulin, Acts on liver & It helps body to utilise glucose
Can help you to lose some weight
Initially, it may cause upset stomach and diarrhoea but usually get better after about 1 week, taking with food can help
Sometimes you might see its empty shell in toilet
Helps to increase the level of insulin secretion from pancreas depending on your glucose levels
Do not cause hypoglycemia & it is the safest drug
These tell the beta cells in pancreas to make more insulin
Sometimes it may cause low blood sugars or Hypoglycemia
They are taken by subcutaneous route like insulin & it helps to increase the level of insulin secretion from the level of insulin secretion from pancreas depending on the blood glucose level
It helps to lower body weight
It does not cause hypoglycemia but sometimes you may feel nausea
It helps in increase glucose uptake by body, especially in your muscle
Sometimes it may cause weight gain or swelling
These are short acting drugs and it helps in insulin secretion by pancreas
These medications should be taken along with meal only
Sometimes it may cause hypoglycemia but chances are less compared to sulfonylureas
These pills slow down the absorption of carbohydrates from the gut after you eat
Have to take it with the meal, since it works on food directly. Skip taking it if you skip a meal
Initially, It may cause some gastric irritation, which generally disappears with time
They work on kidney by throwing glucose out of the body through urine
Can help people to lose some weight
Sometimes it may cause fungal infections in private parts

Hypoglycemia is a condition characterised by abnormally low blood glucose levels, usually less than 70 mg/dl.
This can happen if you:
- Do over exercise
- Don’t eat enough
- Skip a meal
- Take too many medicines
However, it is important to talk to your health care provider about your individual blood glucose targets, and what level is too low for you.
When You Have Low Blood Sugar First, eat or drink 15 grams of a fast-acting carbohydrate, such as:
- Three to four glucose tablets
- One tube of glucose gel
- Four to six pieces of hard candy (not sugar-free)
- 1/2 cup fruit juice
- 1 cup skim milk
- 1/2 cup soft drink (not sugar-free)
- Shaking
- Sweating
- Dizziness
- Hunger
- Fast heartbeat
- Blurry vision
- Headache
- Weakness or fatigue
If you have a low blood sugar problem, it’s important to eat or drink 15 grams of fast acting sugary food right away, such as;
- ½ can of regular (not diet!) soda
- 1 tablespoon (or two packets of a real sugar)
- 3 hard candies that you can eat quickly
Nocturnal hypoglycemia or night time hypos are common in people who treat their diabetes with insulin. Symptoms are usually only realised once waking up from a hypo.
Due to their nature, you will usually only find out about having a hypo during the night after waking up from a hypo.
Therefore people may not even be aware that they are having night time hypos, so it’s useful to be able to spot the signs and symptoms of when nocturnal hypoglycemia may be taking place.
Whilst nocturnal hypoglycemia is most common in insulin users, it can also occur for people who take oral anti-diabetic drugs.
Sometimes you may wake during an episode of nocturnal hypoglycemia.
However, if you don’t, you may notice one or more of the following indications that hypoglycemia may have occurred whilst you were asleep.
- Restless sleep
- Vivid dreams or nightmare
- Morning headache
- Night sweats
- Mood changes
- Fatigue
- Convulsions
For parents of children with diabetes, nocturnal hypoglycemia can be particularly worrying.
Parents of diabetic children may wish to check their child’s neck whilst they are sleeping if they are worried that night time hypoglycemia may be occurring.